Table of Contents
You've probably heard it repeatedly—eat more omega-3s for better health. Whether it’s from your cardiologist, nutritionist, or the latest health blog, there’s a buzz around this essential nutrient. But amidst all the noise, two questions might arise: What exactly are omega-3 fatty acids? And why are they deemed so vital for our health?
Dive into our comprehensive guide as we demystify omega-3 fatty acids, shedding light on their significance and offering practical tips on enhancing your intake for optimal health.
Understanding Omega-3: Why is it Essential?
Omega-3s belong to a group of beneficial dietary fats, playing pivotal roles in maintaining the integrity and function of every cell in our bodies. These fatty acids wear many hats: they're not just a part of cellular structures but are also involved in myriad activities at cellular and system-wide levels.
Interestingly, our bodies cannot produce omega-3s autonomously despite their importance. This categorizes them as an "essential" nutrient. Simply to harness the benefits of omega-3s, one must rely on omega-3-rich foods and supplements.
Discover the Main Types of Omega-3s: Why They Matter
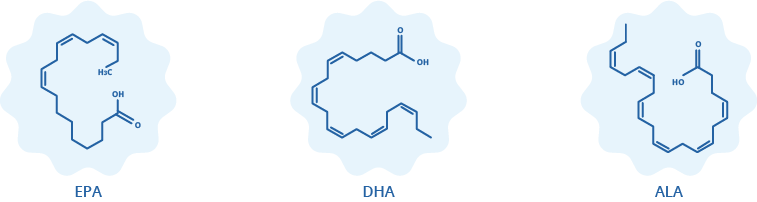
Omega-3s are not just a singular entity; there are multiple varieties. DHA, EPA, and ALA are the three powerhouses in this category that are fundamental to our health. Here's a breakdown:
1. DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
DHA isn't just any ordinary omega-3. It is the predominant omega-3 in your brain, making up over 90% of its omega-3 content. This fatty acid is crucial for cognitive function and brain development. Plus, you can find DHA playing a protective role in your skin and eyes. And if that wasn’t enough, it also boasts anti-inflammatory properties.*
2. EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)
While EPA may share anti-inflammatory benefits with DHA, it's distinct in its own right. It's instrumental in promoting overall body health, highlighting the importance of incorporating it into your diet.*
3. ALA (Alpha-linolenic Acid)
You're likely to consume ALA if you’re a fan of plant-based foods like nuts, seeds, and certain vegetables. While the body only converts a modest amount of ALA to DHA and EPA, this conversion underscores its importance in supporting cellular development and various physiological functions.
The Broad Spectrum of Omega-3 Benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially the dynamic duo of DHA and EPA, are not just essential nutrients but champions for our health. Here's a breakdown of the numerous health benefits they provide:

1. Counteracting Inflammation
While inflammation is a natural immune response, chronic inflammation is a silent culprit behind ailments like arthritis and even severe conditions such as heart disease and Type 2 diabetes. The anti-inflammatory compounds in both DHA and EPA can potentially modulate this response, ensuring our immune system acts as a guardian rather than an aggressor.*
2. Heart Health
Beyond combating inflammation, DHA and EPA serve as sentinels for our hearts. They assist in regulating blood pressure, decreasing elevated triglyceride levels, and minimizing the risk of blood clots—making them valuable allies in the quest for cardiovascular well-being.*
3. Nurturing the Brain
Given that DHA is integral to our brain structure, its sufficient intake is necessary for optimal brain health. For expectant mothers, omega-3s are pivotal to support the neural development of their babies. Furthermore, increasing omega-3 consumption has ties to combating depression, lowering ADHD risk, and thwarting neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer's.*
4. Fortifying Bones and Muscles
Your skeletal and muscular systems also benefit from omega-3s. Research suggests a link between these fatty acids and the prevention of bone-related issues. Incorporating DHA and EPA into the diet is a wise move for fitness enthusiasts or those aiming to maintain muscle mass, given their involvement in muscle protein synthesis.*
Omega-3 Intake: How Much is Right for You?
The recommended daily intake of omega-3s is not a one-size-fits-all answer. It varies based on age, gender, health, and even life stages like pregnancy. Here’s a concise guide:
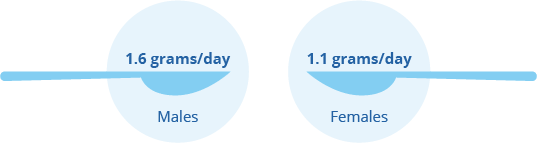
Standard Daily Recommendations
- Males: 1.6 grams/day
- Females: 1.1 grams/day
For specific circumstances:
- Pregnant Women: 1.4 grams/day
- Breastfeeding Women: 1.3 grams/day
Beyond the Basics: Omega-3 Types
While these numbers provide a general idea, it's crucial to understand the types of omega-3s in your diet. DHA and EPA offer more direct benefits than ALA since ALA needs conversion. For individuals with coronary heart disease, the American Heart Association suggests:
- EPA+DHA: About 1 gram/day
- ALA: 1.5-3 grams/day, though evidence leans more favorably toward EPA and DHA benefits.
The Risks of Omega-3 Deficiency
Missing out on these essential fats can trigger symptoms such as:

- Dryness in skin, hair, eyes
- Joint aches
- Mental fog
- Mood fluctuations like depression
Long-term, a low omega-3 diet can pave the way for inflammatory conditions, given its balancing act with omega-6 fatty acids. A diet overpowered by omega-6, commonly found in foods like meats and certain oils, can lean towards inflammation and heart complications. Striking a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 intake can shield against these inflammatory ailments.
Omega-3, particularly DHA, is paramount for those pregnant or considering pregnancy. It supports babies' optimal brain and eye development, making its intake essential during this critical period.
Where to get Omega-3s
Omega-3s play a vital role in our health. But where can you get them? And how can you ensure a sustainable intake? Here's everything you need to know.

1. Fish-based Omega-3s: DHA and EPA
Cold-water fish, like tuna and mackerel, are rich in DHA and EPA. Their immense omega-3 content has led to the popularity of supplements such as fish oil and cod liver oil pills. For many, these supplements are a convenient alternative to regular fish consumption.
Other meats like beef and poultry also offer omega-3s but aren't as potent.
The Challenges with Fish-based Omega-3s
Not everyone can, or wants to, rely on fish for their omega-3 intake. Vegans, vegetarians, and those with fish allergies need alternatives. Moreover, the environmental impact of overfishing, propelled in part by the demand for fish oil pills, makes it imperative to explore sustainable sources.
2. Plant-Powered Omega-3s: ALA
The plant kingdom offers ALA, a precursor to DHA and EPA. Some ALA-rich sources include:
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseed oil
- Walnuts
- Kale
- Brussels sprouts
- Hemp seeds
The Challenges with Plant-based ALA
However, the ALA to DHA and EPA conversion rate in the human body is inefficient, hovering below 5%. Consequently, relying solely on these sources might not meet omega-3 intake needs. Some might argue that plant-based supplements, like vegan flaxseed oil, can bridge the gap. Yet, they face the same conversion challenge.
3. The Ideal Plant-based Alternative: Algae Oil
Algae, specifically microalgae, present an exciting solution. They naturally produce DHA and EPA, drawing energy from sunlight. Interestingly, the high DHA and EPA content in cold-water fish is due to their diet of microalgae. Therefore, algae oil supplements are a promising, sustainable, and effective alternative for those wanting DHA and EPA without fish consumption.

Is Omega-3 Supplementation Right for You?
Omega-3 fatty acids are heralded for their myriad of health benefits. But with the typical Western diet often lacking in sufficient omega-3s, it leaves a gap that supplements might fill. Among these, vegan algae oil supplements are emerging as a sustainable and practical choice.
When to Consider an Omega-3 Supplement:
- Seafood Consumption: If you’re not consuming enough oily fish regularly, or you're looking to decrease your consumption for environmental reasons, a supplement might be necessary.
- Dietary Choices: Vegans and vegetarians might not get enough omega-3s due to their dietary restrictions.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Omega-3s are essential for fetal brain development and maternal health.*
- Heart Health: Want to bolster your cardiovascular system? Omega-3s are known to assist with their heart-protective benefits.*
- Balancing Omega Ratios: A diet high in omega-6 fatty acids but low in omega-3s might warrant supplementation.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, including algae oil pills. They can provide insights into your omega-3 needs, potential interactions, and the ideal dosage tailored to you.