Table of Contents
A well-balanced, nutritious diet is essential for maintaining health, and one key component is healthy fats, especially omega-3s. These polyunsaturated fatty acids have many health benefits, including heart, brain, and skin health, immune function, and their association with longevity.
Omega-3s can be found in foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, many people struggle to consume enough through their diet alone. This challenge has contributed to the rise in popularity of supplements, such as fish oil and algae oil capsules.
To fully harness the benefits of omega-3s, it's important to meet recommended daily intake levels. So, how much omega-3 should you consume daily to optimize your health?
Why Omega-3s Are "Essential"
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats. The body does not produce sufficient amounts of these fats, so they must be obtained through diet or supplements, making them "essential."
Sources of omega-3 include fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as plant-based options like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Omega-3s are also found in supplements.
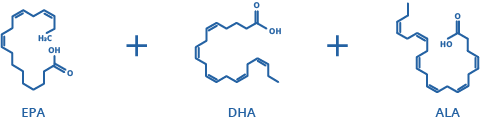
The three main types of omega-3 fatty acids that are crucial for your diet include:
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid): Essential for brain development and renowned for its anti-inflammatory benefits.*
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid): Helps reduce blood clotting and possesses anti-inflammatory properties.*
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid): Found in select plant-based foods, it must be converted into DHA or EPA before your body can utilize it effectively.
The Health Benefits of Omega-3s
Omega-3s are celebrated for their many benefits, especially their ability to reduce inflammation, support development, and maintain heart and cognitive health.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), two prominent types of omega-3s found in fish oil, are renowned for their cardiovascular benefits. They've been shown to help lower triglyceride levels, reduce blood pressure, and decrease the risk of heart disease.
Omega-3s also have anti-inflammatory effects that have been shown to alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases.
They also help support brain health, aid in cognitive function and memory retention, and potentially reduce the risk of cognitive decline in older adults.
Additionally, there's evidence suggesting that omega-3 supplementation can aid in developmental support during pregnancy, promote healthier skin, and contribute to a balanced sleep cycle.*
How Much Omega-3 Per Day?

There isn’t currently enough evidence to set an official recommended daily intake of omega-3s.
However, health organizations have provided general guidelines for "adequate intakes" (AI) of omega-3s, which is the amount needed to prevent health problems caused by a low intake.
According to the Dietary Reference Intake from the National Academy of Medicine, the AI for omega-3 is:
- For adult men: Approximately 1.6 grams of EPA and DHA combined per day.
- For women of reproductive age: Approximately 1.1 grams of combined EPA and DHA per day.
These recommendations are based on the average needs of healthy people. However, requirements can vary depending on factors such as age, health status, and dietary habits.
For example, pregnant and breastfeeding women often require more omega-3 to support fetal brain development as well as their own immune function and brain and heart health. According to the American Pregnancy Association, pregnant women should consume about 200–300 milligrams of omega-3s per day, including at least 200 mg of DHA.
Your Needs for EPA/DHA Vs. ALA:
If you're wondering about the amount of omega-3s you should be consuming daily, a better question would be how much EPA and/or DHA per day you require.
When you see the term “omega-3”, such as on food labels or supplements, it doesn’t necessarily refer to EPA/DHA. And since EPA and DHA are the more beneficial forms of omega-3s compared to ALA, this distinction is crucial when selecting omega-3 supplements.
Here's how much EPA/DHA to aim for each day:
- The American Heart Association recommends consuming around 1 gram of combined EPA and DHA daily. Evidence suggests that achieving this intake can reduce mortality linked to heart disease.*
- Pregnant women benefit from consuming an average of 200 mg of DHA daily to support fetal development.*
If you have an existing health condition or if you're pregnant or nursing, it's best to speak with your healthcare provider about the specific dosage they recommend taking.
How To Get Enough Omega-3s
Incorporating omega-3 into your daily diet can be achieved through a variety of foods and supplements. Here's are some of the different sources that are available:
Fatty Fish:
Aim to consume fatty and oil fish like salmon, trout, mackerel, and sardines at least two to three times per week. An average serving to aim for is about 3 ounces, or the size of a deck of cards.
The fish below are rich sources of EPA and DHA, making them the best foods to boost your omega-3 intake:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Trout
- Herring
- Anchovies
- Albacore Tuna
Plant-Based Sources:
Vegetarians and vegans who don't eat fish and seafood can still obtain omega-3s from their diets.
Plant-based sources of omega-3s include flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts, as well as algae (organisms that harness energy directly from sunlight and absorb nutrients directly from the water).
It's important to note that these foods contain high amounts of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a precursor to EPA and DHA, although conversion rates in the body are relatively low.
To meet your omega-3 intake goals, you would need to consume a substantial amount of ALA-rich foods daily. Therefore, relying solely on a plant-based diet may not suffice to obtain adequate omega-3s.
A more effective solution is to supplement with a vegan-friendly option that provides sufficient EPA and DHA without using fish oils, such as algae oil capsules.*
Omega-3 Supplements:
Omega-3 supplements, including fish oil and algae oil capsules, provide a concentrated dose of EPA and DHA.
What is Algae oil?
Oily fish accumulate omega-3s by consuming algae, which are primary producers of these beneficial fatty acids. Algae oil supplements offer a promising alternative to traditional fish oil pills, catering to plant-based diets. By taking algae oil supplements, you directly obtain EPA and DHA from the same source as fish.*

These supplements are advantageous because they are:
- Plant-based: Derived from microalgae, these photosynthetic organisms are rich in EPA and DHA, which are crucial for their anti-inflammatory properties and overall health benefits.
- Environmentally friendly: Algae oil supplements are sustainable and do not contribute to overfishing or harm marine ecosystems, unlike traditional fish oil products.*
Overall, algae oil makes an excellent fish oil alternative for vegetarians, vegans, and people unable to consume fish or fish oil, helping to ensure they meet their omega-3 needs effectively.*
Note: To obtain the most benefits from omega-3 supplements, look for those that are third-party tested for purity and free from contaminants like heavy metals and PCBs, such as our Sustainable Vegan Omega-3s.
Signs You Might Need More Omega-3
If you experience any of the symptoms below frequently, it may be a sign that you're experiencing low levels of omega-3s and could benefit from adding more to your diet or supplement routine:
- Dry skin: Omega-3s help maintain skin hydration and elasticity. Dry, flaky skin may indicate a deficiency.
- Joint pain and aches: Inflammatory conditions like arthritis may benefit from the anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Mood swings: Omega-3s play a role in brain function and mood regulation. Deficiencies may contribute to mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
It's recommended that you consult with a healthcare provider if you suspect you might have an omega-3 deficiency or are considering supplementation. They can assess your needs based on your health history and recommend appropriate adjustments to your diet as well as supplements to support your health goals.
Can You Take Too Many Omega-3s?
While it’s important to meet your omega-3 needs, and more specifically your requirement for EPA and DHA, consuming more isn’t necessarily better for your health.

In fact, excessive intake of omega-3s can potentially weaken the immune system and disrupt normal responses to inflammation.*
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to acute illnesses and injuries. Adequate inflammation is necessary for healing and recovery. However, excessive omega-3 intake may suppress the immune system, making you more susceptible to acute illnesses and potentially prolonging recovery time.*
Exceeding your daily omega-3 intake limit can also increase bleeding tendencies (since EPA reduces blood clotting) and potentially elevate the risk of stroke.
Therefore, always follow omega-3 dosage recommendations, or if your doctor recommends a specific amount, avoid taking more to reduce the risk of interactions or side effects.
Key Takeaways on How Many Omega-3s You Need & Best Sources
- Meeting your daily recommended intake of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, supports your overall health in many ways.
- Omega-3s are found in oily fish, some nuts and seeds, and supplements like fish oil and algae oil.
- Choosing algae oil supplements provides a sustainable and beneficial alternative to fish-derived sources.
References:
- https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(22)00639-1/abstract
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/01.ATV.0000057393.97337.AE
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564314/
- https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/benefits-of-fish-oil-supplements-fish-consumption/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33231984/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38427239/#:~:text=Omega%2D3%20fatty%20acids%20play,working%20of%20the%20nervous%20system.
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/fish-and-omega-3-fatty-acids
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18184094/